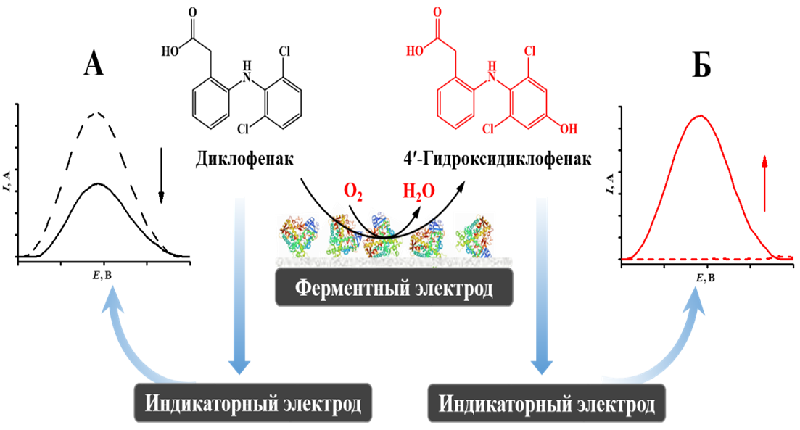

Figure 3. Two-electrode system for recording substrates or metabolites of cytochrome P450-dependent reactions. The principle of bielectrode electrochemical systems based on the use of an enzyme electrode with immobilized recombinant cytochrome P450 (or a membrane-bound form of this protein) and an indicator electrode on which the loss of substrate (A) or increase in product (B) is quantitatively determined by registration the electrochemical oxidation of these compounds during different potentials. As an example, an enzyme electrode with immobilized CYP2C9 is presented, which hydroxylates the marker substrate diclofenac with the formation of the reaction product 4ʹ-hydroxydiclofenac.