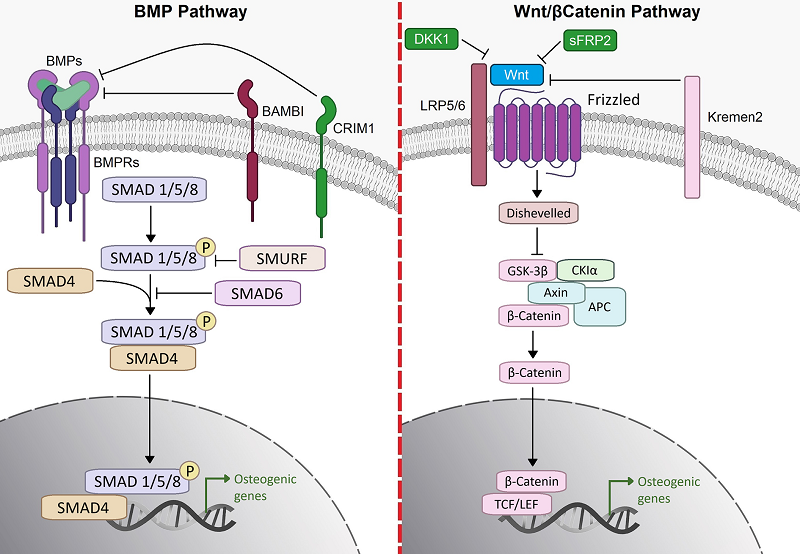

Figure 3. Conventional osteogenic differentiation pathways. Cartoon showing the two classical osteogenic differentiation pathways of MSCs/preosteoblasts, i.e., the bone morphogenic pathway and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. BMPRs—BMP receptors; BAMBI—BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor homolog; CRIM1—cysteine-rich motor neuron 1 protein; SMAD—small mothers against decapentaplegic; DKK1—Dickkopf-related protein 1; sFRP2—secreted frizzled-related protein 2; Kremen—Kringle domain-containing transmembrane protein; LRP—Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein; GSK—glycogen synthase kinase; CKIα—casein kinase Iα; APC—adenomatous polyposis coli; TCF/LEF—T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor [23]. In the nucleus, β-catenin activates transcription factors (T-cell factor/lymphoid factor lead to activation of target gene expression).