Steroidal Inhibitors of CYP17A1 as a Template For Novel Anti-Cancer Agents Development
Institute of Biomedical Chemistry, 8119121 Pogodinskaya Str., 10 bldg. 8, Moscow, Russia,*e-mail: alexander.misharin@ibmc.msk.ru
Keywords: CYP17A1 inhibitors; abiraterone; galeterone; nitrogen-containing steroidal derivatives; anti-proliferative activity; anti-cancer activity
DOI: 10.18097/BMCRM00020
This review deals with studies of researches of novel CYP17A1 steroidal inhibitors and relative compounds published over the last ten years. The review contains six chapters in which novel targets of well-known CYP17A1 inhibirors (abiraterone and galeterone), anti-cancer and anti-proliferative activities of them major metabolites and new synthetic analogs, and in addition another nitrogen-containing androstane and pregnane derivatives are considered. In the review 354 structures of novel steroid derivatives and them anti-cancer efficiency data are considered. Analysis of the literature data allows us to consider steroidal inhibitors of CYP17A1 as multi-target anti-cancer agents with high pharmacological potential.
|
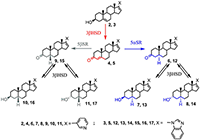
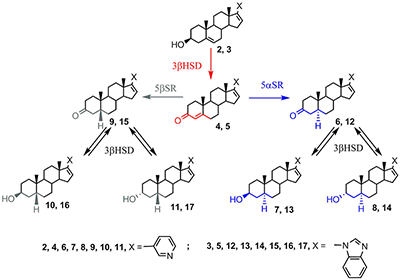
Figure 1.
Metabolism of abiraterone and galeterone. 5αSR - 5α-reductase; 5β-reductase, 3βHSD - 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
|
Oxazoline comprising [17(20)E]-21-norpregnene derivative 296 inhibited СYP17A1 catalytic activity more potently than abiraterone; changes of the oxazoline fragment for 4,4-dimethyl oxazoline (297) and benzoxazole (301) reduced inhibiting potency by one and two orders of magnitude, respectively [64-66]. [17(20)E]-21-Norpregnene derivatives comprising either polar (299 and 300), or bulky (298) substituents at C4’ in the oxazoline moiety did not bind to enzyme and did not demonstrate any inhibiting potency [40,65].

Among analogs of oxazoline comprising derivative 296 differing in structures of А and B rings, the most potent inhibiting activity exhibited 3-keto-4-еn- and seco-A-derivatives (302, 303). The removal of oxygen containing group at C3, its substitution for chloro- or methoxy- function, as well as introducing of ketogroup into C6 position, led to non active compounds 305-309 [66].

The inhibitory potency of oxazolines towards CYP17A1 activity as well as their ability to inhibit of prostate carcinoma LNCaP and РС-3 cells growth was decreased in the following row: 296 > 303 > 302. (Table 1).
|
CLOSE

|
Table 1.
Biological activity of compounds 296-309
|
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was performed within the framework of the State Academies of Sciences Fundamental Research Program for 2013–2020.
REFERENCES
- Huggins, C. & Hodges, C. V. (1941). Studies on Prostatic Cancer. I. The Effect of Castration, of Estrogen and of Androgen Injection on Serum Phosphatases in Metastatic Carcinoma of the Prostate. Cancer Reseach, 1(4), 293-297.
- Huggins, C, Stevens R. E., Hodges C. V. (1941). Studies on prostatic cancer: II. The effects of castration on advanced carcinoma of the prostate gland. Archives of surgery. 43(2), 209–223. DOI
- Kan, P. B.; Hirst, M. A.; Feldman, D. (1985). Inhibition of steroidogenic cytochrome P-450 enzymes in rat testis by ketoconazole and related imidazole anti-fungal drugs. Journal Steroid Biochemistry, 23(6A), 1023-1029. DOI
- de Bono, J. S., Logothetis, C. J., Molina, A., Fizazi, K., North, S., Chu, L., et al. (2011). Abiraterone and increased survival in metastatic prostate cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 364, 1995–2005. DOI
- Handratta, V.D., Vasaitis, T.S., Njar, V.C.O., Gediya, L.K., Kataria, R., Chopra, P., Newman, D., Farquhar, R., Guo, Z., Qiu, Y., Brodie, A.M.H. (2005). Novel C-17-heteroaryl steroidal CYP17 inhibitors/antiandrogens: Synthesis, in vitro biological activity, pharmacokinetics, and antitumor activity in the LAPC4 human prostate cancer xenograft model. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 48, 2972–2984. DOI
- Clement, O. O., Freeman, C. M., Hartmann, R. W., Handratta, V. D., Vasaitis, T. S., Brodie, A. M. H., Njar, V. C. O. (2003). Three dimensional pharmacophore modeling of human CYP17 inhibitors. Potential agents for prostate cancer therapy. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 46 (12), 2345–2351. DOI
- DeVore, N. M. & Scott, E. E. (2012). Cytochrome P450 17A1 structures with prostate cancer drugs Abiraterone and TOK-001. Nature, 482(7383), 116–119. DOI
- Njar, V. C., Brodie, A. M. (1999). Inhibitors of 17a-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase (CYP17): potential agents for the treatment of prostate cancer. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 5, 163–180.
- Hartmann, R. W., Ehmer, P.B., Haidar, S., Hector, M., Jose, J., Klein, C. D. P., et al. (2002). Inhibition of CYP 17, a new strategy for the treatment of prostate cancer. Archiv der Pharmazie, 4, 119–128.
- Bruno, R.D., Njar, V.C. (2007). Targeting cytochrome P450 enzymes: a new approach in anti-cancer drug development. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 15(15), 5047–60. DOI
- Baston, E., Leroux, F.R. (2007). Inhibitors of steroidal cytochrome P450 enzymes as targets for drug development. Recent Patents on Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery, 2(1), 31–58. DOI
- Moreira, V. M., Salvador, J. A. R, Vasaitis, T.S., Njar, V.C.O. (2008). CYP17 Inhibitors for Prostate Cancer Treatment – An Update. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 15, 868-899. DOI
- Owen, C. P. (2009). 17α-Hydroxylase/17,20-Lyase (P45017α) Inhibitors in the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 9, 613-626. DOI
- Vasaitis, T. S., Bruno, R. D., Njar, V. C. O. (2011). CYP17 inhibitors for prostate cancer therapy. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 125, 23–31. DOI
- Salvador, J. A. R., Pinto, R. M. A., Silvestre, S. M. (2013). Steroidal 5α-reductase and 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase (CYP17) inhibitors useful in the treatment of prostatic diseases. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 137, 199–222. DOI
- Salvador, J. A. R., Moreira, V. M., Silvestre, S. M. (2012). Steroidal CYP17 Inhibitors for Prostate Cancer Treatment: From Concept to Clinic. INTECH. Chapter 12. DOI
- Auchus, M. L., Auchus, R. J. (2012). Human steroid biosynthesis for the oncologist. Journal of Investigative Medicine, 60(2), 495-503. DOI
- Yin, L. & Hu, Q. (2014). CYP17 inhibitors - abiraterone, C17,20-lyase inhibitors and multi-targeting agents. Nature Reviews Urology, 11, 32-42. DOI
- Malikova, J., Brixius-Anderko, S., Udhane, S. S., Parween, S., Dick, B., Bernhardt, R., Pandey, A. V. (2017). CYP17A1 inhibitor abiraterone, an anti-prostate cancer drug, also inhibits the 21-hydroxylase activity of CYP21A2. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 174, 192-200. DOI
- Mostaghel, E.A., Marck, B., Plymate, S., Vessella, R. L., Balk, S. P., Matsumoto, A. M., Nelson, P. S., Montgomery, R. B. (2011). Resistance to CYP17A1 inhibition with abiraterone in castration resistant prostate cancer: Induction of steroidogenesis and androgen receptor splice variants. Clinical Cancer Research, 17(18), 5913–5925. DOI
- Yip, C. K.Y., Bansal, S., Wong, S. Y., Lau, A. J. (2018). Identification of Galeterone and Abiraterone as Inhibitors of Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfonation Catalyzed by Human Hepatic Cytosol, SULT2A1, SULT2B1b, and SULT1E1. Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 46(4); 470-482. DOI
- Udhane, S. S., Dick, B., Hu, Q., Hartmann, R. H., Pandey, A. V. (2016). Specificity of anti-prostate cancer CYP17A1 inhibitors on androgen biosynthesis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 477(4), 1005-1010. DOI
- Pia, A., Vignani, F., Attard, G., Tucc,i M., Bironzo, P., Scagliotti, G., Arlt, W., Terzolo, M. & Berruti, A. (2013). Strategies for managing ACTH dependent mineralocorticoid excess induced by abiraterone. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 39(8), 966-973. DOI
- Richards, J., Lim, A. C., Hay, C. W., Taylor, A. E, Wingate, A., Nowakowska, K., Pezaro, C., Carreira, S., Goodall, J., Arlt, W., McEwan, I. J., de Bono, J. S., Attard, G. (2012). Interactions of abiraterone, eplerenone, and prednisolone with wild-type and mutant androgen receptor: a rationale for increasing abiraterone exposure or combining with MDV3100. Cancer Research. 72(9), 2176-2182. DOI
- Norris, J. D., Ellison, S. J., Baker, J. G., Stagg, D. B., Wardell, S.E., Park, S., Alley, H. M., Baldi, R. M., Yllanes, A., Andreano, K. J., Stice, J. P., Lawrence, S. A., Eisner, J. R., Price, D. K., Moore, W. R., Formulag, W. D., McDonnell, D. P. (2017). Androgen receptor antagonism drives cytochrome P450 17A1 inhibitor efficacy in prostate cancer. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 127(6), 2326-2338. DOI
- Bonnefoi, H., Grellety, T., Tredan, O., Saghatchian, M., Dalenc, F., Mailliez, A., L'Haridon, T., Cottu, P., Abadie-Lacourtoisie, S., You, B., Mousseau, M., Dauba, J., Del Piano, F., Desmoulins, I., Coussy, F., Madranges, N., Grenier. J., Bidard, F.C., Proudhon, C., MacGrogan, G., Orsini, C., Pulido, M., Gonçalves, A. (2016). A phase II trial of abiraterone acetate plus prednisone in patients with triple-negative androgen receptor positive locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer (UCBG 12-1). Annals of Oncology, 27(5), 812-818. DOI
- Banerjee, S., Kilburn, L., Bowen, R., Tovey, H., Hall, M., Kaye, S., Rustin, G., Gore, M., McLachlan, J., Attygalle, A., Tunariu, N., Lima, J. P., Chatfield, P., Jeffs, L., Folkerd, E., Hills, M., Perry, S., Attard, G., Dowset, M., Bliss, J. (2016). Principal results of the cancer of the ovary abiraterone trial (CORAL): A phase II study of abiraterone in patients with recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer (CRUKE/12/052). Annals of Oncology, 27(6), LBA33. DOI
- Njar, V. C., Brodie, A. M. (2015). Discovery and development of Galeterone (TOK-001 or VN/124-1) for the treatment of all stages of prostate cancer. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 58(5), 2077-2087. DOI
- Dransfield, D. T., Namdev, N., Jacoby, D. B., Ferrante, K. (2016). Correlation of galeterone-induced degradation of the androgen receptor with inhibition of a deubiquitinating enzyme. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 34(2_suppl), 345-345. DOI
- Hupe, M. C., Offermann, A., Perabo, F., Chandhasin, C., Perner, S., Merseburger, A. S., Cronauer, M. V. (2018). Inhibitoren des Androgenrezeptor-N-Terminus’ Zielgerichtete Therapien gegen die Achillesferse verschiedener Androgenrezeptormoleküle im fortgeschrittenen Prostatakarzinom. Der Urologe, 57(2), 148–154. DOI
- Grossebrummel, H., Peter, T., Mandelkow, R., Weiss, M., Muzzio, D., Zimmermann, U., Walther, R., Jensen, F., Knabbe, C., Zygmunt, M., Burchardt, M., Stope, M. B. (2016). Cytochrome P450 17A1 inhibitor abiraterone attenuates cellular growth of prostate cancer cells independently from androgen receptor signaling by modulation of oncogenic and apoptotic pathways. International Journal of Oncology, 48(2), 793-800. DOI
- Kwegyir-Afful, A.K., Ramalingam, S., Purushottamachar, P., Ramamurthy, V. P., Njar, V. C. (2015). Galeterone and VNPT55 induce proteasomal degradation of AR/AR-V7, induce significant apoptosis via cytochrome c release and suppress growth of castration resistant prostate cancer xenografts in vivo. Oncotarget, 6(29), 27440-27460. DOI
- Kwegyir-Afful, A. K., Bruno, R. D., Purushottamachar, P., Murigi, F.N., Njar, V. C. (2016). Galeterone and VNPT55 disrupt Mnk-eIF4E to inhibit prostate cancer cell migration and invasion. FEBS Journal, 283(21), 3898-3918. DOI
- Kwegyir-Afful, A. K., Murigi, F. N., Purushottamachar, P., Ramamurthy, V. P., Martin, M. S., Njar, V. C. O. (2017). Galeterone and its analogs inhibit Mnk-eIF4E axis, synergize with gemcitabine, impede pancreatic cancer cell migration, invasion and proliferation and inhibit tumor growth in mice. Oncotarget, 8(32), 52381–402. DOI
- Li, Z., Bishop, A. C., Alyamani, M., Garcia, J. A., Dreicer, R., Bunch, D., Liu, J., Upadhyay, S. K., Auchus, R. J., Sharifi, N. (2015). Conversion of abiraterone to D4A drives anti-tumour activity in prostate cancer. Nature, 523 (7560), 347-351. DOI
- Alyamani, M., Li, Z., Berck, M., Li, J., Tang, J., Upadhyay, S., Auchus, R. J., Sharifi, N. (2017). Steroidogenic metabolism of galeterone reveals a diversity of biochemical activities. Cell Chemical Biology. 2017, 24(7), 1-8. DOI
- Li, R., Evaul, K., Sharma, K. K., Chang, K. H., Yoshimoto, J., Liu, J., Auchus, R. J., Sharifi, N. (2012). Abiraterone Inhibits 3β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase: A Rationale for Increasing Drug Exposure in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer, Clinical Cancer Research, 18, 3571–3579. DOI
- Garrido, M., Peng, H. M., Yoshimoto, F. K., Upadhyay, S.K., Bratoeff, E., Auchus, R. J. (2014). A-ring modified steroidal azoles retaining similar potent and slowly reversible CYP17A1 inhibition as abiraterone. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 143, 1–10. DOI
- Li, Z., Alyamani, M., Li, J., Rogacki, K., Abazeed, M., Upadhyay, S. K., Balk, S. P., Taplin, M.-E., Auchus, R. J., Sharifi, N. (2016). Redirecting abiraterone metabolism to fine tune prostate cancer anti-androgen therapy. Nature, 533(7604), 547-551. DOI
- Kostin, V. A., Zolottsev, V. A., Kuzikov, A. V., Masamrekh, R. A., Shumyantseva, V. V., Veselovsky, A. V., Stulov, S. V., Novikov, R. A., Timofeev, V. P., Misharin, A. Y. (2016). Oxazolinyl derivatives of [17(20)E]-21-norpregnene differing in the structure of A and B rings. Facile synthesis and inhibition of CYP17A1 catalytic activity. Steroids, 115, 114–122. DOI
- Brossard, D., Zhang, Y., Haider, S. H., Sgobba, M., Khalid, M., Legay, R., Duterque-Coquillaud, M., Galera, P., Rault, S., Dallemagne, P., Moslemi, S., El Kihel, S. (2013). N-substituted Piperazinopyridylsteroid Derivatives as Abiraterone Analogues Inhibit Growth and Induce Pro-apoptosis in Human Hormone-independent Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Chemical Biology & Drug Design, 82(5), 620–629. DOI
- Purushottamachar, P., Godbole, A. M., Gediya, L. K., Martin, M. S., Vasaitis, T. S., Kwegyir-Afful, A. K., Ramalingam, S., Ates-Alagoz, Z., Njar, V. C. O. (2013). Systematic Structure Modifications of Multitarget Prostate Cancer Drug Candidate Galeterone To Produce Novel Androgen Receptor Down-Regulating Agents as an Approach to Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Journal of Мedicinal Сhemistry, 56(12), 4880-4898. DOI
- Purushottamachar, P., Kwegyir-Afful, A. K., Martin, M. S., Ramamurthy, S., Ramalingam, S., Njar, V. C. O. (2016). Identification of Novel Steroidal Androgen Receptor Degrading Agents Inspired by Galeterone 3β-Imidazole Carbamate. ACS Мedicinal Сhemistry Letters, 7(7), 708-713. DOI
- Banday, A. H., Mira, B. P., Khazir, J., Suri, K. A., Kumar, H. M. S. (2010). Studies on novel D-ring substituted steroidal pyrazolines as potential anticancer agents. Steroids, 75(12), 805-809. DOI
- Banday, A. H., Akram, S. M. M., Parveen, R., Bashir, N. (2014). Design and synthesis of D-ring steroidal isoxazolines and oxazolines as potential antiproliferative agents against LNCaP, PC-3 and DU-145 cells. Steroids, 87, 93-98. DOI
- Ondre, D., Wolfling, J., Toth, I., Szecsi, M., Julesz, J., Schneider, G. (2009). Steroselective synthesis of some steroidal oxazolines, as novel potential inhibitors of 17α-hydroxylase-C17,20-lyase. Steroids, 74(13-14), 1025–1032. DOI
- Wolfling, J., Oravecz, E. A., Ondre, D., Mernyak, E., Schneider, G., Toth, I., Szecsi, M., Julesz, J. (2006). Stereoselective synthesis of some 17beta-dihydrooxazinyl steroids, as novel presumed inhibitors of 17α-hydroxylase-C17,20-lyase., Steroids, 71(9), 809–816. DOI
- Banday, A. H., Shameem, S. A., Jeelani, S. (2014). Steroidal pyrazolines and pyrazoles as potential 5a-reductase inhibitors: Synthesis and biological evaluation. Steroids, 92, 13–19. DOI
- Ivanyi, Z., Wolfling, J., Gorbe, T., Szecsi, M., Wittmann, T., Schneider, G. (2010). Synthesis of regioisomeric 17β-N-phenylpyrazolyl steroid derivatives and their inhibitory effect on 17α-hydroxylase/C17,20-lyase. Steroids, 75(6), 450–456. DOI
- Ivanyi, Z., Szabo, N., Huber, J., Wolfling, J., Zupko, I., Szecsi, M., Wittmann, T., Schneider, G. (2012). Synthesis of D-ring-substituted (5’R)- and (5’S)-17β-pyrazolinylandrostene epimers and comparison of their potential anticancer activities. Steroids, 77(5), 566-574. DOI
- Ivanyi, Z., Szabo, N., Wolfling, J., Szecsi, M., Julesz, J., Schneider, G. (2012). Novel series of 17β-pyrazolylandrosta-5,16-diene derivatives and their inhibitory effect on 17α-hydroxylase/C17,20-lyase. Steroids, 77(11), 1152-1159. DOI
- Szabo, N., Ivanyi, Z., Szecsi, M., Julesz, J., Mernyak, E., Huber, J., Wolfling, J., Minorics, R., Zupko, I., Schneider, G. (2015). Synthesis of methoxycarbonylpyrazolylandrostene derivatives, and their potential inhibitory effect on androgen biosynthesis and cell proliferation. Steroids, 98, 143–152. DOI
- Kiss, A., Herman, B. E., Gorbe, T., Mernyak, E., Molnar, B., Wolfling, J., Szecsi, M., Schneider, J. (2018). Synthesis of novel 17-triazolyl-androst-5-en-3-ol epimers via Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition and their inhibitory effect on 17α-hydroxylase/C17,20-lyase. Steroids. DOI
- Silva-Ortiza, A. V., Bratoeff, E., Ramírez-Apan, M. T., García-Becerra, R., Ordaz-Rosado, D., Noyola-Martínez, N., Castillo-Bocanegra, R., Barrera, D. (2016). Synthesis and biological activity of two pregnane derivatives with a triazole or imidazole ring at C-21. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 159, 8–18. DOI
- Silva-Ortiz, A. V., Bratoeff, E., Ramírez-Apan, T., Heuze, Y., Sánchez, A., Soriano, J., Cabeza, M., (2015). Synthesis and activity of novel 16-dehydropregnenolone acetate derivatives as inhibitors of type 1 5α-reductase and on cancer cell line SK-LU-1. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 23(24), 7535-7542. DOI
- Silva-Ortiz, A. V., Bratoeff, E., Ramírez-Apan, T., Heuze, Y., A., Soriano, J., Moreno, I., Bravo, M., Bautista, L., Cabeza, M. (2017). Synthesis of new derivatives of 21-imidazolyl-16-dehydropregnenolone as inhibitors of 5α-reductase 2 and with cytotoxic activity in cancer cells. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 25(5), 1600-1607. DOI
- Banday, A. H., Shameen, S. A., Gupta, B. D., Kumar, H. M. S. (2010). D-ring substituted 1,2,3-triazolyl 20-keto pregnenanes as potential anticancer agents: Synthesis and biological evaluation. Steroids, 75(12), 801-804. DOI
- Szabó, N., Ajduković, J. J., Djurendić, E. A., Sakač, M. N., Ignáth, I., Gardi, J., Mahmoud, G., Klisurić, O. R., Jovanović-Šanta, S., Penov Gaši, K. M., Szécsi, M. (2015). Determination of 17α-hydroxylase-C17,20-lyase (P450 17α) enzyme activities and their inhibition by selected steroidal picolyl and picolinylidene compounds. Acta Biologica Hungarica, 66(1), 41–51. DOI
- Djurendic, E., Ajducovic, J. J., Sakac, M., Csanadi, J., Kojic, V., Bogdanovic, G., Penov Gasi, K. (2012). Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of some 17-picolyl and 17-picolinylidene androstane derivatives. European journal of medicinal chemistry, 54, 784-792. DOI
- Ajducovic, J. J., Djurendic, E., Petri, E. T., Klisuric, O., Celic, A., Sakac, M., Jakimov, D., Penov Gasi, K. (2013). 17(E)-Picolinylidene androstane derivatives as potential inhibitors of prostate cancer cell growth: Antiproliferative activity and molecular docking studies. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 21(23), 7257–7266. DOI
- Jakimov, D. S., Kojic, V. V., Aleksic, L. D., Bogdanovic, G. M., Ajdukovic, J. J., Djurendic, E. A., Penov Gaši, K. M., Sakac, M. N., Jovanović-Šanta, S. S. (2015). Androstane derivatives induce apoptotic death in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 23(22), 7189–7198. DOI
- Gasi, K, M, Djurendic-Brenesel, M., Djurendic, E., Sakac, M., Csanadi, J., Daljev, J., et al. (2007). Synthesis and biological evaluation of some 17-picolyl and 17-picolinylidene androst-5-ene derivatives. Steroids, 72(1), 31–40. DOI
- Djurendic, E., Daljev, J., Sakac, M., Csanadi, J., Jovanovic-Santa, S., Andric, S., Klisuric, O., Kojic, V., Bogdanovic, G., Djurendic-Brenesel, M., Novakovic, S., Penov Gasi, K. (2008). Synthesis of some epoxy and/or N-oxy 17-picolyl and 17-picolinylidene androst-5-ene derivatives and evaluation of their biological activity. Steroids; 73(1), 129–138. DOI
- Kuzikov, A. V., Dugin, N. O., Stulov, S. V., Shcherbinin, D. S., Zharkova, M. S., et al. (2014). Novel oxazolinyl derivatives of pregna-5,17(20)-diene as 17a-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase (CYP17A1) inhibitors, Steroids, 88, 66–71. DOI
- Stulov, S. V., Dugin, N. O., Zharkova, M. S., Shcherbinin, D. S., Kuzikov, A. V., Shumantseva V. V., Misharin, A. Yu., Veselovsky, A. V. (2015). Interaction of Novel Oxazoline Derivatives of 17(20)E-pregna-5,17(20)-Diene with Cytochrome P450 17A1 Biochemistry (Moscow) Supplement Series B: Biomedical Chemistry, 9(2), 114–120. DOI
- Zolottsev, V. A., Tkachev, Y. V., Latysheva, A. S., Kostin, V. A., Novikov, R. A., Timofeev, V. P., Morozevich, G. E., Kuzikov, A. V., Shumyantseva, V. V., Misharin, A. Y. (2018). Comparison of [17(20)E]-21-Norpregnene oxazolinyl and benzoxazolyl derivatives as inhibitors of CYP17A1 activity and prostate carcinoma cells growth. Steroids, 129, 24–34. DOI
- Moreira, V. M. A., Vasaitis, T. S., Guo, Z., Njar, V. C. O, Salvador, J. A. R. (2008). Synthesis of Novel C17 Steroidal Carbamates. Studies on CYP17 Action, Androgen Receptor Binding and Function, and Prostate Cancer Cell Growth. Steroids, 73(12), 1217-1227. DOI
- Nikolić, A. R., Petri, E. T., Klisurić, O. R., Ćelić, A. S., Jakimov, D. S., Djurendić, E. A., Penov Gaši, K. M., Sakač, M. N. (2015). Synthesis and anticancer cell potential of steroidal 16,17-seco-16,17a-dinitriles: Identification of a selective inhibitor of hormone-independent breast cancer cells. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 23(4), 703-711. DOI
- Cortes-Benítez, F., Cabeza, M., Ramírez-Apan, M. T., Alvarez-Manrique, B., Bratoeff, E. (2016). Synthesis of 17β-N-arylcarbamoylandrost-4-en-3-one derivatives and their anti-proliferative effect on human androgen-sensitive LNCaP cell line. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 121, 737-746. DOI
- Bratoeff, E., Garrido, M., Ramírez-Apan, M. T., Heuze, M., Sanchez, A., Soriano, J., Cabeza, M. (2014). Effect of dehydroepiandrosterone derivatives on the activity of 5α-reductase isoenzymes and on cancer cell line PC-3. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 22(21), 6233-6241. DOI
- Aggarwal, S., Thareja, S., Verma, A., Bhardwaj, T. R., Kumar, M. (2010). An overview on 5α-reductase inhibitors. Steroids, 75(2), 109-153. DOI
- Schmidt, L. J., Tindall, D. J. (2011). Steroid 5α-reductase inhibitors targeting BPH and prostate cancer. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 125(1-2), 32–38. DOI
- Vihko, P., Herrala, A., Harkonen, P., Isomaa, V., Kaija, H., Kurkela, R., Pulkka, A. (2006). Control of cell proliferation by steroids: the role of 17HSDs. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 248(1-2), 141-148. DOI
- Day, J., Tutill, H., Purohit, A., Reed, M. (2008). Design and validation of specific inhibitors of 17{beta}-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases for therapeutic application in breast and prostate cancer, and in endometriosis. Endocrine-Related Cancer, 15(3), 665-692. DOI
- Poirier, D. (2003). Inhibitors of 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 10(6), 453-77.
- Poirier, D. (2009). Advances in Development of Inhibitors of 17β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenases. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 9, 642-60. DOI
- Poirier, D. (2010). 17beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors: a patent review. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents, 20(9), 1123-1145. DOI
- Jegham, H., Maltais, R., Roy, J., Doillon, C., Poirier, D. (2012). Biological evaluation of a new family of aminosteroids that display a selective toxicity for various malignant cell lines. Anticancer Drugs, 23(8), 803–814. DOI
- Maltais, R., Tremblay, M. R., Ciobanu, L. C., Poirier, D. (2004). Steroids and combinatorial chemistry. Journal of Combinatorial Chemistry, 6(4), 443-456. DOI
- Poirier, D. (2008). New cancer drugs targeting the biosynthesis of estrogens and androgens. Drug Development Research, 69(6), 304-318. DOI
- Frank, E., Schneider, G. (2013). Synthesis of sex hormone-derived modified steroids possessing antiproliferative activity. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 301– 315. DOI