The 40th Anniversary of the Institute of Physiologically Active Compounds of the Russian Academy of Sciences
Effect of Endogenous Peptides on the Currents of NMDA- and AMPA-Receptors of Neurons of The Cortex, Hippocampus and Cerebellum of Rat Brain
Institute of Physiologically Active Compounds of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 1 Severny proezd, Moscow region, Chernogolovka, 142432 Russia;*e-mail: bovina_e@ipac.ac.ru
Key words: NMDA- and AMPA-receptors; delta-sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP); corticotropin-like intermediate frontal peptide (CLIP); somatostatin; uridine; muramyl dipeptides (MDP)
DOI: 10.18097/BMCRM00021
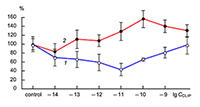
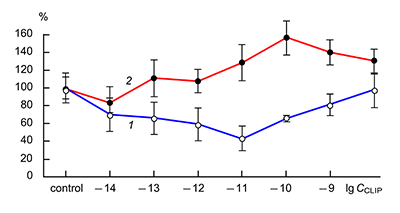
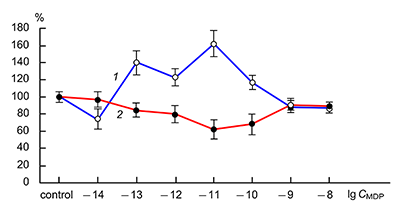
The obtained results show that endogenous peptides play an important role in the regulation of the glutamatergic mediator system of the brain. They act in extremely low concentrations, starting at 1 × 10–14 M, their effects are concentration-dependent and reversible, thus indicating the exclusive specificity of the corresponding receptors. The range of their influence on responses of postsynaptic glutamate receptors is rather narrow and, as a rule, does not exceed 60-70% of control. We have demonstrated for the first time that CLIP blocks NMDA receptors and potentiates AMPA receptors in a wide range of concentrations (6 orders of magnitude); this is very important for manifestation of memory-stimulating effect. Somatostatin blocking NMDA receptors and potentiating AMPA receptors, also plays an important role in the mechanisms of memory formation. Obviously, there is a great similarity in the action of both peptides on AMPA and NMDA receptors. Thus our results provide the first information about regulation of including cognitive processes and memory mechanisms by endogenous compounds. This mechanism particularly involves regulation of AMPA and NMDA receptors in the brain.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The study was conducted in accordance to the Research Topic no. 48.8 «The search and determination of the mechanisms of neuroprotectors and stimulators of cognitive functions» in the framework of the State Task of the Institute of Physiologically Active Compounds of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Topic: No: 0090-2017-0019).
The equipment of the Centre of the collective usage of IPAC RAS has been used in the work (Agreement No. 14.621.21.0008, work identifier RFMEFI62114X0008).
REFERENCES
- Umriukhin, P. E. (2002). Delta sleep-inducing peptide blocks excitatory effects of glutamate on rat brain neurons. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 134(1), 5-7, DOI
- Hamill, O. P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F. J. (1981). Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology, 391(2), 85-100, DOI
- Kaneda, M., Nakamura, H., Akaike, N. (1988). Mechanical and enzymatic isolation of mammalian CNS neurons. Neuroscience Research, 5(4), 299-315, DOI
- Grigor'ev, V. V., Ivanova, T. A., Kustova, E. A., Petrova, L. N., Serkova, T. P., Bachurin, S. O. (2006). Effects of delta sleep-inducing peptide on pre- and postsynaptic glutamate and postsynaptic GABA receptors in neurons of the cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum in rats. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 142(2), 186-8, DOI
- Grigoriev, V. V., Petrova, L. N., Ivanova, T. A., Gabreliyan, A. V., Serkova, T. P. (2009). Effect of corticotropin-like intermediate lobe peptide on presynaptic and postsynaptic glutamate receptors and postsynaptic GABA receptors in rat brain. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 147(3), 319-322, DOI
- Grigoriev, V. V., Petrova, L. N., Gabrelian, A. V., Zamoyski, V. L., Serkova, T. P., Bachurin, S. O. (2012). Effect of somatostatin on presynaptic and postsynaptic glutamate receptors and postsynaptic GABA receptors in the neurons of rat brain. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 154(1), 10-12, DOI
- Grigoriev, V. V., Petrova, L. N., Gabreliyan, A. V., Ivanova, T. A. (2008). Effect of muramyl dipeptides on postsynaptic GABA, NMDA, and AMPA receptors and presynaptic NMDA receptors in rat brain. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 146(3),. 276-278, DOI
- Stanojlovic, O. P., Zivanovic, D. P., Mirkovic, S. D., Mikhaleva, I. I. (2005). Antiepileptic activity of delta sleep-inducing peptide and its analogue in metaphit-provoked seizures in rats. Seizure, 14(4), 240-247, DOI
- Kimura, T., Ho, I. K., Yamamoto, I. (2001). Uridine receptor: discovery and its involvement in sleep mechanism. Sleep, 24(3), 251-260.
- Rauchs, G., Bertran, F., Guillery-Girard, B., Desgranges, B., Kerrouche, N., Denise, P., Foret, J., Eustache, F. (2004). Consolidation of strictly episodic memories mainly requires rapid eye movement sleep. Sleep, 27(3), 395-401, DOI
- Wetzel, W., Balschun, D., Janke, S., Vogel, D., Wagner, T. (1994). Effects of CLIP (corticotropin-like intermediate lobe peptide) and CLIP fragments on paradoxical sleep in rats. Peptides, 15(2), 237-241, DOI
- Matsuoka, N., Maeda, N., Yamaguchi, I., Satoh, M. (1994). Possible involvement of brain somatostatin in the memory formation of rats and the cognitive enhancing action of FR121196 in passive avoidance task. Brain Research, 642(1-2), 11-119, DOI
- Tallent, M. K., Siggins, G. R. (1997). Somatostatin depresses excitatory but not inhibitory neurotransmission in rat CA1 hippocampus. Journal of Neurophysiology, 78(6), 3008-3018, DOI
- Ambrosini, M. V., Giuditta, A. (2001). Learning and sleep: the sequential hypothesis. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 5(6), 477-490 DOI
- Wetzel, W., Wagner, T., Balschun, D. (2003). REM sleep enhancement induced by different procedures improves memory retention in rats. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 18(9), 2611-2617, DOI