New Nitrogen-Containing Androstane Derivatives Suppressing Prostate Carcinoma Cells Proliferation
1Institute of Biomedical Chemistry, 10 Pogodinskaya str., Moscow, 119121 Russia; *e-mail: aidanlinch@gmail.com
2Engelhardt Institute of Molecular Biology, Russian Academy of Sciences, 32 Vavilov str., Moscow, 119991 Russia
Keywords: nitrogen-containing steroid derivatives; prostate carcinoma cells; CYP17A1 inhibitors; synthesis of steroid derivatives; antiproliferative activity; molecular docking
DOI:10.18097/BMCRM00241
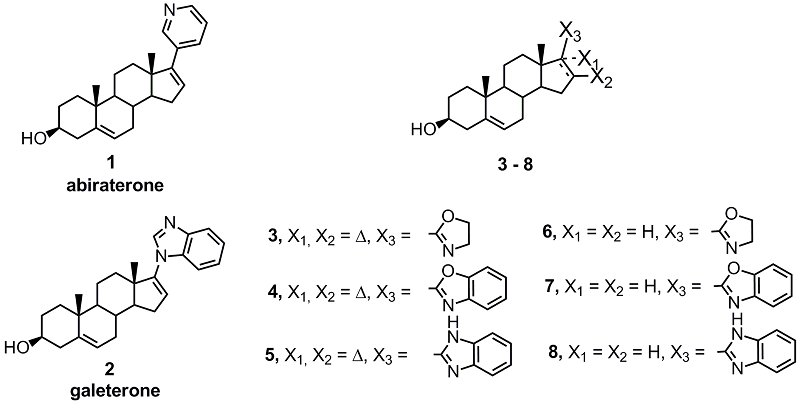
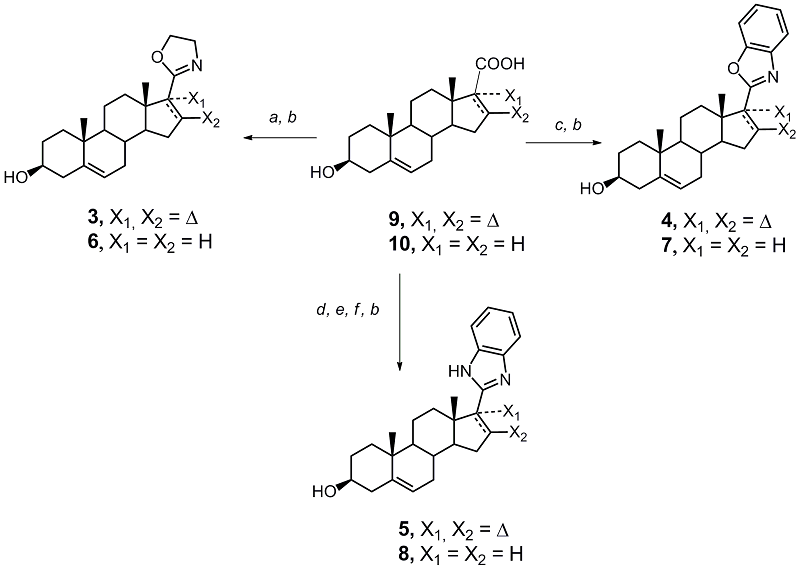
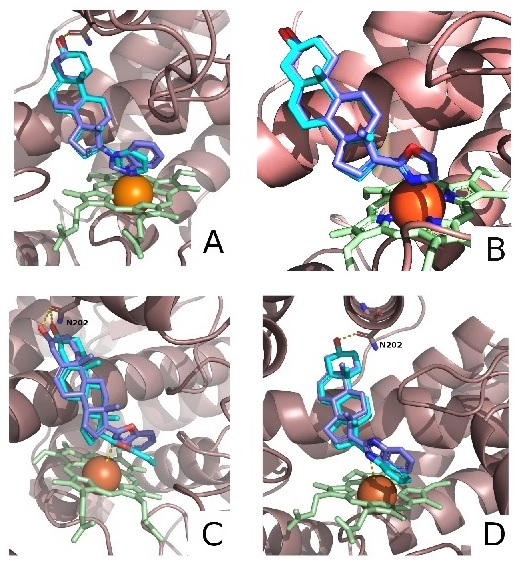
Derivatives of 3β-hydroxyandrost-5,16-diene and 3β-hydroxyandrost-5-ene containing 2-oxazoline, 2-benzoxazole, and 2-benzimidazole substituents at C-17 position were synthesized. Docking of the synthesized compounds into the active site of human CYP17A1 predicted their high affinity for the enzyme. Of the 6 new compounds, 5 suppressed the proliferation of prostate carcinoma cells LNCaP and PC-3, and the activity of the oxazoline and benzimidazole derivatives of androsta-5,16-diene significantly exceeded the activity of the known anticancer agents abiraterone and galeterone.
FUNDING
The work was performed within the framework of the Program for Basic Research in the Russian Federation for a long-term period (2021-2030) (no. 122030100170-5).
REFERENCES
- Ling, Y.Z., Li, J.S., Liu, Y., Kato, K., Klus, G.T., Brodie, A. (1997) 17-Imidazolyl, pyrazolyl, and isoxazolyl androstene derivatives. Novel steroidal inhibitors of human cytochrome C17,20-lyase (P450(17 alpha). J. Med. Chem., 40(20), 3297–3304. DOI
- Njar, V.C.O., Kato, K., Nnane, I.P., Grigoryev, D.N., Long, B.J., Brodie, A. (1998) Novel 17-azolyl steroids, potent inhibitors of human cytochrome 17 alpha-hydroxylase-C17,20-lyase (P450(17) alpha): Potential agents for the treatment of prostate cancer. J. Med. Chem., 41(6), 902–912. DOI
- Njar, V.C., Brodie, A.M. (1999) Inhibitors of 17alphahydroxylase/ 17,20-lyase (CYP17): Potential agents for the treatment of prostate cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des., 5(3), 163–180.
- Zhu, N., Ling, Y., Lei, X., Handratta, V., Brodie, A.M.H. (2003) Novel P450(17alpha) inhibitors: 17-(2′-oxazolyl)- and 17-(2′-thiazolyl)-androstene derivatives. Steroids, 68(7–8), 603–611. DOI
- Bruno, R.D., Njar, V.C. (2007) Targeting cytochrome P450 enzymes: A new approach in anti-cancer drug development. Bioorg Med. Chem., 15(15), 5047–5060. DOI
- Baston, E., Leroux, F.R. (2007) Inhibitors of steroidal cytochrome P450 enzymes as targets for drug development. Recent. Pat. Anticancer. Drug Discov., 2(1), 31–58. DOI
- Potter, G.A., Barrie, S.E., Jarman, M., Rowlands, M.G. (1995) Novel steroidal inhibitors of human cytochrome P45017 alpha (17 alpha-hydroxylase-C17,20-lyase): Potential agents for the treatment of prostatic cancer. J. Med. Chem., 38(13), 2463–2471. DOI
- Handratta, V.D., Vasaitis, T.S., Njar, V.C., Gediya, L.K., Kataria, R., Chopra, P., Newman, D. Jr., Farquhar, R., Guo, Z., Qiu, Y., Brodie, A.M. (2005) Novel C-17-heteroaryl steroidal CYP17 inhibitors/antiandrogens: Synthesis, in vitro biological activity, pharmacokinetics, and antitumor activity in the LAPC4 human prostate cancer xenograft model. J. Med. Chem., 48(8), 2972–2984. DOI
- Njar, V.C., Brodie, A.M. (2015) Discovery and development of Galeterone (TOK-001 or VN/124-1) for the treatment of all stages of prostate cancer. J. Med. Chem., 58(5), 2077–2087. DOI
- Hartmann, R.W., Ehmer, P.B., Haidar, S., Hector, M., Jose, J., Klein, C.D., Seidel, S.B., Sergejew, T.F., Wachall, B.G., Wächter, G.A., Zhuang, Y. (2002) Inhibition of CYP 17, a new strategy for the treatment of prostate cancer. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim), 335(4), 119–128. DOI
- Salvador, J.A., Pinto, R.M., Silvestre, S.M. (2013) Steroidal 5α-reductase and 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase (CYP17) inhibitors useful in the treatment of prostatic diseases. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 137, 199–222. DOI
- Salvador, J.A.R., Moreira, V.M., Silvestre, S.M. (2013) Steroidal CYP17 Inhibitors for Prostate Cancer Treatment: From Concept to Clinic. Chapter 12 In: Advances in Prostate Cancer (Hamilton, G., ed.); InTech, 704 p. DOI
- Bird, I.M., Abbott, D.H. (2016) The hunt for a selective 17,20 lyase inhibitor; learning lessons from nature. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 163, 136–146. DOI
- Stulov, S.V., Misharin, A.Y. (2013) Synthesis of steroids with nitrogen-containing substituents in ring D. Chem. Heterocycl. Comp., 48, 1431–1472. DOI
- Singh, R., Panda, G. (2013) An overview of synthetic approaches for heterocyclic steroids, Tetrahedron, 69(14), 2853–2884. DOI
- Owen, C.P. (2009) 17alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase (p450(17alpha)) inhibitors in the treatment of prostate cancer: A review. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem., 9(6), 613–626. DOI
- Vasaitis, T.S., Bruno, R.D., Njar, V.C. (2011) CYP17 inhibitors for prostate cancer therapy. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 125(1–2), 23–31. DOI
- Latysheva, A.S., Misharin, A.Yu. (2018) Steroidal inhibitors of CYP17A1 — the template for novel anti-cancer agents development. Biomedical Chemistry: Research and Methods, 1(2), e00020. DOI
- Latysheva, A.S., Zolottsev, V.A., Pokrovsky, V.S., Khan, I.I., Misharin, A.Y. (2021) Novel nitrogen containing steroid derivatives for prostate cancer treatment. Curr. Med. Chem., 28(40), 8416–8432. DOI
- Huo, H., Li, G., Shi, B., Li, J. (2022) Recent advances on synthesis and biological activities of C-17 aza-heterocycle derived steroids. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 69, 116882. DOI
- Kostin, V.A., Zolottsev, V.A., Kuzikov, A.V., Masamrekh, R.A., Shumyantseva, V.V., Veselovsky, A.V., Stulov, S.V., Novikov, R.A., Timofeev, V.P., Misharin, A.Y. (2016) Oxazolinyl derivatives of [17(20)E]-21-norpregnene differing in the structure of A and B rings. Facile synthesis and inhibition of Cyp17A1 catalytic activity. Steroids, 115, 114–122. DOI
- Zolottsev, V.A., Kostin, V.A., Novikov, R.A., Tkachev, Ya.V., Zavialova, M.G., Taratynova, M.O., Latysheva, A.S., Zazulina, O.V., Timofeev, V.P., Misharin, A.Yu. (2018) Synthesis of nitrogen-containing derivatives of 17(20)-pregnenoic, 17β-hydroxypregnanoic, and 17α-hydroxypregnanoic acids as new potential antiandrogens. Russ. Chem. Bull., 67, 667–681. DOI
- Kostin, V.A., Latysheva, A.S., Zolottsev, V.A., Tkachev, Ya.V., Timofeev, V.P., Kuzikov, A.V., Shumyantseva, V.V., Morozevich, G.E., Misharin, A.Yu. (2018) Oxazoline derivatives of [17(20)E]-21- norpregnene – inhibitors of CYP17A1 activity and proliferation of prostate carcinoma cells. Russ. Chem. Bull., 67, 682–687. DOI
- Zolottsev, V.A., Tkachev, Y.V., Latysheva, A.S., Kostin, V.A., Novikov, R.A., Timofeev, V.P., Morozevich, G.E., Kuzikov, A.V., Shumyantseva, V.V., Misharin, A.Y. (2018) Comparison of [17(20)E]-21-norpregnene oxazolinyl and benzoxazolyl derivatives as inhibitors of CYP17A1 activity and prostate carcinoma cells growth. Steroids, 129, 24-34. DOI
- Staunton, J., Eisenbraun, E.J. (1962) 3β-Acetoxyetienic acid [3β-Acetoxy-5-androstene-17β-carboxylic acid]. Org. Synth., 42, 4. DOI
- Trott, O., Olson, A.J. (2010) AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem., 31(2), 455–461. DOI:10.1002/jcc.21334
- Salentin, S., Schreiber, S., Haupt, V.J., Adasme, M.F., Schroeder, M. (2015) PLIP: Fully automated protein-ligand interaction profiler. Nucleic Acids Res., 43(1), 443–447. DOI
- Mosmann, T. (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods, 65(1–2), 55–63. DOI
- Grossebrummel, H., Peter, T., Mandelkow, R., Weiss, M., Muzzio, D., Zimmermann, U., Walther, R., Jensen, F., Knabbe, C., Zygmunt, M., Burchardt, M., Stope, M.B. (2016) Cytochrome P450 17A1 inhibitor abiraterone attenuates cellular growth of prostate cancer cells independently from androgen receptor signaling by modulation of oncogenic and apoptotic pathways. Int. J. Oncol., 48(2), 793–800. DOI
- Bruno, R.D., Gover, T.D., Burger, A.M., Brodie, A.M., Njar, V.C. (2008) 17alpha-Hydroxylase/17,20 lyase inhibitor VN/124-1 inhibits growth of androgen-independent prostate cancer cells via induction of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Mol. Cancer Ther., 7(9), 2828–2836. DOI