The 40th Anniversary of the Institute of Physiologically Active Compounds of the Russian Academy of Sciences
QSAR Modeling of the NMDA Receptor Blockage by Polypharmacophoric Compounds Based on Carbazole and 1-aminoadamantane Derivatives
Institute of Physiologically Active Compounds of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 1 Severny proezd, Moscow region, Chernogolovka, 142432 Russia;*e-mail: beng@ipac.ac.ru
Key words: QSAR; NMDAR; polypharmacophoric compounds
DOI: 10.18097/BMCRM00064
We investigated 14 compounds causing the NMDA receptor blockage. These polypharmacophoric compounds are conjugates of carbazole, tetrahydrocarbazole and 1-aminoadamantane derivatives. As a measure of biological activity of the compound tested, the IC50 (μM) value, reflecting 50% inhibition of [H3] MK-801 binding to the NMDA receptor, was used. The regression model with satisfactory statistical characteristics was obtained as a result of the QSAR modeling based on the Gaussian process.
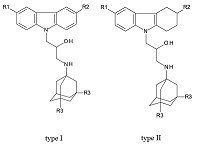

|
Figure 1.
Structural formulas of polypharmacophoric compounds based on carbazoles (type I), tetrahydrocarbazoles (type II) and 1-aminoadamantanes derivatives.
|
|
CLOSE

|
Table 1.
Type and substituents (Figure 1), biological activity (-lg(IC50), μM) and descriptors (D1 ÷ D7) of compounds. |
|
CLOSE

|
Table 2.
Statistical characteristics of QSAR models of the NMDA receptor inhibition.
|
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work was performed within the framework of the state task for 2018 (the topic number 0090-2017-0020).
REFERENCES
- Pangalos, M.N., Schechter, L.E., & Hurko O. (2007) Drug development for CNS disorders: strategies for balancing risk and reducing attrition. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov., 6(7), 521-532. DOI
- Silva, T., Reis, J., Teixeira, J., & Borges F. (2014) Alzheimer’s disease, enzyme targets and drug discovery struggles: from natural products to drug prototypes. Ageing Res. Rev., 15, 116-145. DOI
- Gitto, R., Luca, L.D., Ferro, S.C., Sarro, G.D., Costa, L., Ciranna, L., & Chimirri, A. (2009) Development of 3-substituted-1H-indole derivatives as NR2B/NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 17, 1640-1647. DOI
- Fang, J., Li, Y., Liu, R., Pang, X., Li, C., Yang, R., He, Y., Lian, W., Liu, A., & Du, G. (2015) Discovery of multi-target-directed ligands against Alzheimer’s disease through systematic prediction of chemical-protein interactions. J. Chem. Inf. Model., 55(1), 149-164. DOI
- Raevsky, O.A., Trepalin, S.V., Grigorev, V.Yu., Yarkov, A.V., Bachurin, S.O. (2017) Certificate of state registration of the database "Multitarget organic compounds with potential effects on the central nervous system" ¹ 2017620020.
- HYBOT. Retrieved August 24, 2018, from http://molpro.ipac.ac.ru/hybot.html
- DRAGON. Retrieved August 24, 2018, from http://www.talete.mi.it/products/dragon_projects.htm
- Forsythe, G.E., Malcolm, M.A., Moler, C.B. (1977) Computer Methods for Mathematical Computations, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, Prentice-Hall, 227-235.
- RF. Retrieved August 24, 2018, from http://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/RandomForests/cc_examples/prog.f
- Obrezanova, O., Cs?nyi, G., Gola, J.M.R., & Segall, M.D. (2007) Gaussian processes: a method for automatic QSAR modeling of ADME properties. J. Chem. Inf. Model., 47, 1847-1857. DOI
- Mitra, I., Saha, A., & Roy K. (2010) Exploring quantitative structure–activity relationship studies of antioxidant phenolic compounds obtained from traditional Chinese medicinal plants. Mol. Simul., 36(13), 1067-1079. DOI
- Tropsha, A., Gramatica, P., & Gombar, V.K. (2003) The importance of being earnest: validation is the absolute essential for successful application and interpretation of QSPR models. QSAR Comb. Sci., 21(1), 69–77. DOI