Modified Knottins as Potential Inhibitors of HCV NS3 Protease
Institute of Biomedical Chemistry, 10 Pogodinskaya str., Moscow, 119121 Russia; *e-mail: bionasty@mail.ru
Keywords: HCV NS3/4A protease; knottin; MCOTI-II; molecular dynamics; molecular modeling
DOI:10.18097/BMCRM00235
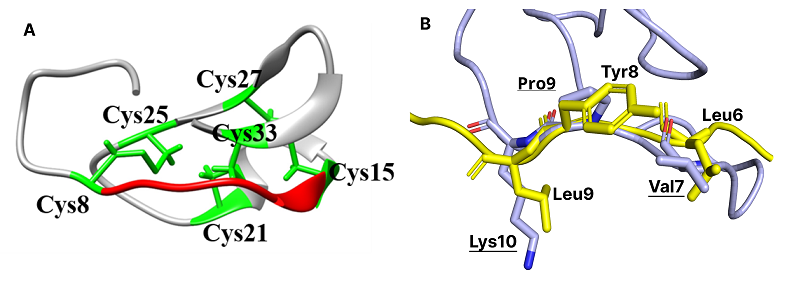
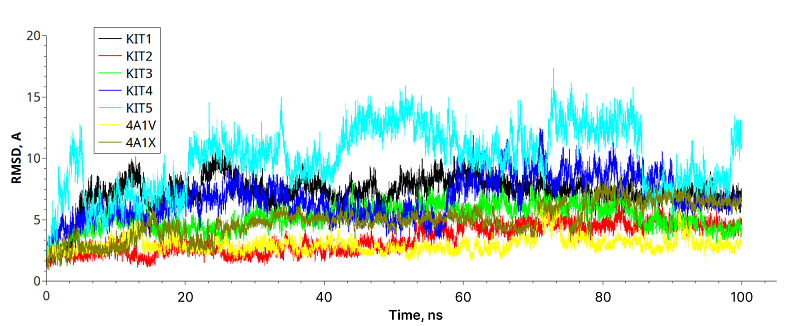
Knottins form a group of peptides containing approximately 30 amino acid residues. Their structures are stabilized by three disulfide bonds forming a characteristic ‘pseudo-knotted’ structure. Several modifications in knottin from Momordica cochinchinensis were made to convert it to inhibitor of human hepatitis C (HCV) NS3 protease. These modifications of the knottin template included deletion of several residues from the N-terminus, replacement of residues in- and outside the inhibitor loop and replacement of certain L-amino acids by their D-stereoisomers. Binding energy values for protein-knottin complexes were estimated by MM-GBSA methods. Two designed knottins showed high stability in knottin-protease HCV complexes and values of binding energy comparable with known peptide inhibitors from crystal structures.
|
CLOSE

|
Table 1.
Sequences of designed knottins. Modifications in KITs in comparison to MCOTI-II are in Italic.
|
|
CLOSE

|
Table 2.
Free binding energy of modified knottins and peptide inhibitors with HCV NS3 protease.
|
FUNDING
The work was performed within the framework of the Program for Basic Research in the Russian Federation for a long-term period (2021-2030) (№ 122030100170-5).
REFERENCES
- Koch, U., Biasiol, G., Brunetti, M., Fattori, D., Pallaoro, M., Steinkuhler, C. (2001) Role of charged residues in the catalytic mechanism of hepatitis C virus NS3 protease: Electrostatic precollision guidance and transition-state stabilization. Biochemistry, 40(3), 631–640. DOI
- Luo, R., Liu, H., Cheng, Z. (2022) Protein scaffolds: Antibody alternatives for cancer diagnosis and therapy. RSC Chem. Biol., 3(7), 830–847. DOI
- Reiss, S., Sieber, M., Oberle, V., Wentzel, A., Spangenberg, P., Claus, R., Kolmar, H., Losche, W. (2006) Inhibition of platelet aggregation by grafting RGD and KGD sequences on the structural scaffold of small disulfide-rich proteins. Platelets, 17(3), 153–157. DOI
- Pope, J.E., Deer, T.R. (2013) Ziconotide: A clinical update and pharmacologic review. Expert Opin. Pharmacother., 14(7), 957–966. DOI
- Castro, J., Harrington, A.M., Hughes, P.A., Martin, C.M., Ge, P., Shea, C.M., Jin, H., Jacobson, S., Hannig, G., Mann, E., Cohen, M.B., MacDougall, J.E., Lavins, B.J., Kurtz, C.B., Silos-Santiago, I., Johnston, J.M., Currie, M.G., Blackshaw, L.A., Brierley, S.M. (2013) Linaclotide inhibits colonic nociceptors and relieves abdominal pain via guanylate cyclase-C and extracellular cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Gastroenterology, 145(6), 1334-1346.e1-11. DOI
- Llinas-Brunet, M., Bailey, M., Fazal, G., Goulet, S., Halmos, T., Laplante, S., Maurice, R., Poirier, M., Poupart, M.A., Thibeault, D., Wernic, D., Lamarre, D. (1998) Peptide-based inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus serine protease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 8(13), 1713–1718. DOI
- Protein Data Bank. http://www.rcsb.org/
- Lindahl, E., Abraham, Hess, B., van der Spoel, D. (2021) Gromacs 2021.1 Manual. DOI
- Case D.A., Darden T., Cheatham T.E. III, Simmerling C., Wang J., Duke R.E., Luo R., Merz K.M., Pearlman D.A.,Crowley M. (2006) AMBER 9. University of California, San Francisco, 45.
- Valdés-Tresanco, M.S., Valdés-Tresanco, M.E., Valiente, P.A., Moreno, E. (2021) gmx_MMPBSA: A new tool to perform end-state free energy calculations with GROMACS. J. Chem. Theory. Comput., 17(10), 6281–6291. DOI
- Kugler, J., Schmelz, S., Gentzsch, J., Haid, S., Pollmann, E., van den Heuvel, J., Franke, R., Pietschmann, T., Heinz, D.W., Collins, J. (2012) High affinity peptide inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus NS3-4A protease refractory to common resistant mutants. J. Biol. Chem., 287(46), 39224–39232. DOI
- Mergler, M., Dick, F., Sax, B., Stahelin, C., Vorherr, T. (2003) The aspartimide problem in Fmoc-based SPPS. Part II. J. Pept. Sci., 9(8), 518–526. DOI